Java8引入的函数式接口是函数式编程的核心特性。使用@FunctionalInterface注解标识,且只包含一个抽象方法的接口称为函数式接口。
📋 四大核心函数式接口
Java8提供了四大核心函数式接口:
| 接口类型 | 方法签名 | 描述 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier | () -> T | 供给型接口 | 不接受参数,返回结果 |
| Consumer | T -> void | 消费型接口 | 接受参数,无返回值 |
| Predicate | T -> boolean | 断定型接口 | 接受参数,返回布尔值 |
| Function<T,R> | T -> R | 函数型接口 | 接受参数,返回结果 |
🏭 Supplier供给型接口
接口定义
java.util.function.Supplier<T> 接口特点:
- 方法签名:
T get() - 函数描述符:
() -> T - 特点:不接受参数,只返回数据
- 用途:类似工厂方法,生产指定结果

实战示例
配置文件读取
/**
* Supplier使用示例
* 读取外部配置文件
*
* @param fileName 文件名
* @return util.Properties
* @author gcoder
* @date 2023-04-21
*/
public static Properties readFile(String fileName) {
Supplier<Properties> supplier = () ->{
try (InputStream is = Test1.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(fileName);) {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(is);
return properties;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
};
return supplier.get();
}作为函数参数使用
/**
* 作为函数参数使用
*
* @param supplier supplier
* @author gcoder
* @date 2023-04-21
*/
public void start(Supplier<String> supplier) {
String s = supplier.get();
System.out.println(s);
}🍽️ Consumer消费型接口
接口定义
java.util.function.Consumer<T> 接口特点:
- 方法签名:
void accept(T t) - 函数描述符:
T -> void - 特点:只接受一个参数,没有返回值
- 用途:对输入参数执行某些操作

实战示例
消费字符串
public static void main(String[] args) {
acceptString("gcoder", s -> {
String[] split = s.split("");
String join = String.join("-", split);
System.out.println("join = " + join);
});
}
/**
* 消费字符串
*
* @param str str
* @param consumer consumer
* @author gcoder
* @date 2023-04-21
*/
public static void acceptString(String str, Consumer<String> consumer) {
consumer.accept(str);
}连续消费字符串
public static void main(String[] args) {
acceptString2("gcoder", s -> {
String[] split = s.split("");
String join = String.join("-", split);
System.out.println("join = " + join);
}, s -> {
System.out.println(s + "第二次消费");
});
}
/**
* 消费字符串
*
* @param str str
* @param consumer1 consumer1
* @param consumer2 consumer2
* @author gcoder
* @date 2023-04-21
*/
public static void acceptString2(String str, Consumer<String> consumer1, Consumer<String> consumer2) {
consumer1.andThen(consumer2).accept(str);
}🔍 Predicate断定型接口
简介
java.util.function.Predicate接口,是一个断定型接口,用于对指定类型的数据进行判断,从而得到一个判断结果(boolean类型的值)。

示例
-
boolean test(T t),用于条件判断
public static void main(String[] args) { boolean test = checkStr("test", s -> s.length() == 4); System.out.println("test = " + test); } /** * 判断字符串 * * @param str str * @param predicate predicate * @return boolean * @author gcoder * @date 2023-04-21 */ public static boolean checkStr(String str, Predicate<String> predicate) { return predicate.test(str); } -
Predicate<T> and(Predicate<? super T> other),用于将两个Prediccate进行逻辑与判断
public static void main(String[] args) { boolean test = checkStr("test", s -> s.length() == 4, s -> s.equals("qwer")); System.out.println("test = " + test); } /** * 多个条件判断字符串 * * @param str str * @param p1 predicate * @param p2 predicate * @return boolean * @author gcoder * @date 2023-04-21 */ public static boolean checkStr(String str, Predicate<String> p1, Predicate<String> p2) { return p1.and(p2).test(str); } -
Predicate<T> negate(),用于取反判断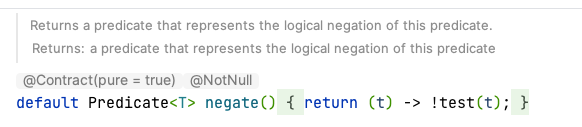
public static void main(String[] args) { boolean test = checkStr2("test", s -> s.length() != 4); System.out.println("test = " + test); } /** * 取反判断字符串 * * @param str str * @param p1 predicate * @return boolean * @author gcoder * @date 2023-04-21 */ public static boolean checkStr2(String str, Predicate<String> p1) { return p1.negate().test(str); } -
Predicate<T> or(Predicate<? super T> other),用于两个Predicate的逻辑”或“判断
public static void main(String[] args) { boolean test = checkStr2("test", s -> s.length() == 4, s -> s.contains("z")); System.out.println("test = " + test); } /** * 多个条件判断字符串 * * @param str str * @param p1 predicate * @param p2 predicate * @return boolean * @author gcoder * @date 2023-04-21 */ public static boolean checkStr2(String str, Predicate<String> p1, Predicate<String> p2) { return p1.or(p2).test(str); }
⚙️ Function函数型接口
接口定义
java.util.function.Function<T,R> 接口特点:
- 方法签名:
R apply(T t) - 函数描述符:
T -> R - 特点:接受一个参数,返回另一个类型的结果
- 用途:根据一个类型的数据得到另外一个类型的数据
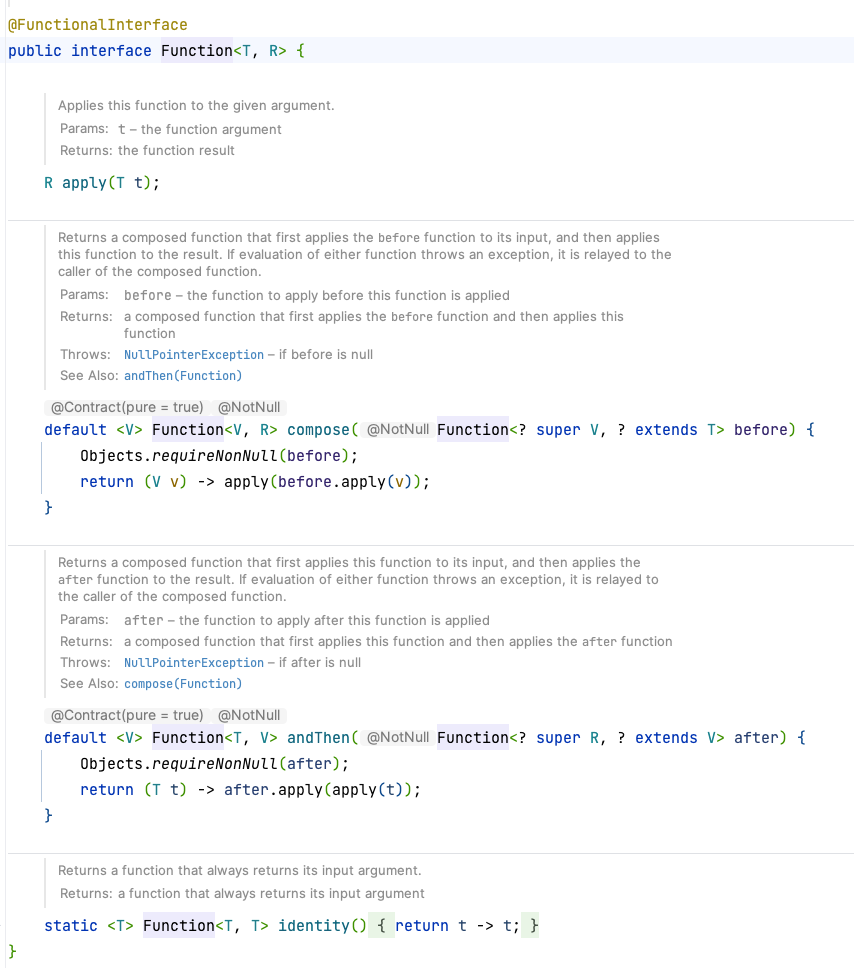
实战示例
-
抽象方法
R apply(T t),根据类型T的参数获取类型R的结果
public static void main(String[] args) { Integer integer = applyMethod("12345", Integer::parseInt); System.out.println("integer = " + integer); } /** * 字符串整数的转换 * * @param str str * @param function function * @return Integer * @author gaohuiwu * @date 2023-04-21 */ public static Integer applyMethod(String str, Function<String, Integer> function) { return function.apply(str); } -
<V> Function<V, R> compose(Function<? super V, ? extends T> before),获取apply的function
public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = applyMethod("12345", s -> s + "777", s -> s + "666"); System.out.println("s1 = " + s1); } /** * 先执行前置函数 * * @param str str * @param f1 function * @param f2 function * @return String * @author gaohuiwu * @date 2023-04-21 */ public static String applyMethod(String str, Function<String, String> f1, Function<String, String> f2) { return f1.compose(f2).apply(str); } -
<V> Function<T, V> andThen(Function<? super R, ? extends V> after),用来进行组合操作,即:”先做什么,再做什么“的场景
public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = applyMethod2("12345", s -> s + "777", s -> s + "666"); System.out.println("s1 = " + s1); } /** * 执行后置函数 * * @param str str * @param f1 function * @param f2 function * @return String * @author gaohuiwu * @date 2023-04-21 */ public static String applyMethod2(String str, Function<String, String> f1, Function<String, String> f2) { return f1.andThen(f2).apply(str); }
📚 总结
以上就是Java8四大核心函数式接口的详细介绍。在实际开发中,合理使用这些函数式接口可以:
优势特点
- ✅ 简化代码:减少复杂的多重if判断
- ✅ 提高可读性:代码更加简洁明了
- ✅ 增强灵活性:函数式编程自由度高
- ✅ 便于测试:独立的函数更容易单元测试
- ✅ 支持链式调用:如
andThen、compose等方法
使用建议
💡 最佳实践:
- 优先使用方法引用(如
Integer::parseInt) - 合理使用Lambda表达式,避免过于复杂的逻辑
- 善用函数式接口的组合方法(
and、or、andThen等) - 在Stream API中大量使用这些函数式接口
函数式编程让我们的代码更加简洁优雅,提升开发效率和代码质量!🚀